by Ardi Mudrayana
Bali’s international airport opened for business Wednesday after a nearly three-day shutdown, as towering columns of volcanic ash and smoke shifted direction on the Indonesian resort island.
The move raised hope for some of the more than 120,000 tourists stranded after a surge in activity at Mount Agung had grounded hundreds of flights since Monday, sparking travel chaos and forcing the evacuation of villagers living in its shadow.
Airport officials cautioned that the airport could shut again if winds change direction once more and endanger flights.
Ash is dangerous for planes as it makes runways slippery and can be sucked into their engines.
“We are going to constantly monitor the situation on the ground,” Ngurah Rai airport spokesman Arie Ahsanurrohim told AFP.
Domestic carrier Garuda said it would start flights to several cities across the vast archipelago nation Wednesday evening, while AirAsia was set to fly to the Malaysian capital Kuala Lumpur.
All other international flights were on standby.
Referring to the Notice to Airmen (NOTAMC) Number: A4300/17 on November 29th, 2017, I Gusti Ngurah Rai Airport is reopen on November 29th, 2017 at 14.28 LT pic.twitter.com/jA3g5Qbmd2
— I Gusti Ngurah Rai (@baliairports) November 29, 2017
Australian tourist Ebra Syllivan was overjoyed at the prospect of getting back home.
“I didn’t know it was going to reopen today — we just came here because our flight was (originally scheduled for) tonight and we’ve booked out of our motel,” she said at the airport.
“It’s fabulous because we need to get back. We’ve got to get back to work.”
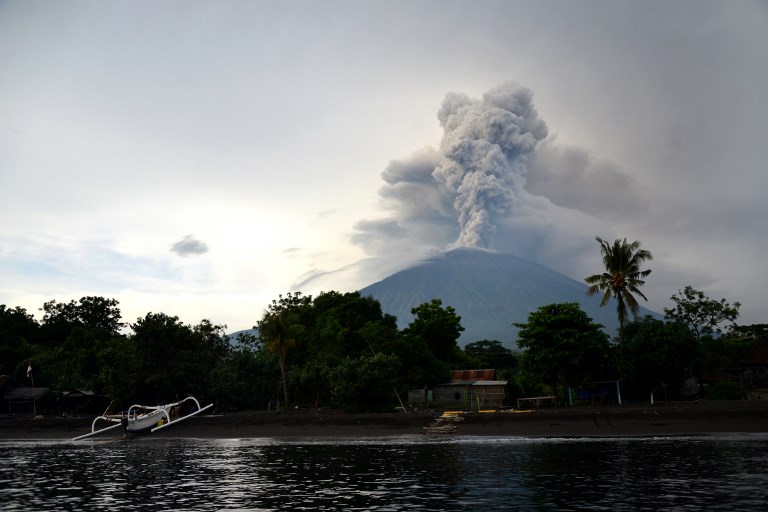
Mount Agung could produce a major eruption at any moment, officials have warned.
‘Bigger, explosive eruption’
Tens of thousands have already fled their homes around the volcano — which last erupted in 1963, killing around 1,600 people — but as many as 100,000 will likely be forced to leave in case a larger eruption comes, disaster agency officials have said.
Experts said Agung’s recent activity matches the build-up to the earlier disaster, which ejected enough debris — about a billion tons — to lower global average temperatures by around 0.3 degrees Celsius for roughly a year.
“Small eruptions have been happening continuously but there’s still the possibility of a bigger, explosive eruption,” said I Gede Suantika, a senior volcanologist at Indonesia’s volcanology agency.
“Activity remains high and we are still on the highest alert level.”
Roadside signs that read “Volcanic danger zone. No entry!” underscored the potential risks of staying behind.
There is a 10 kilometer exclusion zone around Agung, which is 75 kilometers from the beachside tourist hub of Kuta.
As of Wednesday around 440 flights had been cancelled since the start of the week.
The airport on nearby Lombok island — also a popular tourist destination — has opened and closed several times in the past few days. It is currently open.
‘Very nervous’
Some 100 buses were taking visitors to several destinations including Indonesia’s second-biggest city Surabaya on Java island — 13 hours’ drive and a ferry ride away — and the capital Jakarta, as torrential rain lashed the island.
“We decided to take the bus because in this island we are very nervous and we want to stay in another island, we want to be in Java,” said Sofia Maria, a 24-year-old Russian tourist on her way to Jakarta.
The majority of Bali’s tourists are Chinese, followed by Australians, Indians, Britons and Japanese, according to the immigration office, which added that nearly 25,000 foreigners live on the small Hindu-dominated island.
Foreigners whose visitor visas are expiring will be given a special permit to stay longer due to the eruption, the agency said
Agung rumbled back to life in September, forcing the evacuation of 140,000 people living nearby. Its activity decreased in late October and many returned to their homes.
However, on Saturday the mountain sent smoke into the air for the second time in a week in what volcanologists call a phreatic eruption — caused by the heating and expansion of groundwater.
So-called cold lava flows have also appeared — similar to mud flows and often a prelude to the blazing orange lava of popular imagination.
Indonesia, the world’s most active volcanic region, lies on the Pacific “Ring of Fire” where tectonic plates collide, causing frequent volcanic and seismic activities.
Last year seven people were killed after Mount Sinabung on the western island of Sumatra erupted. A 2014 eruption at Sinabung killed 16.




Reader Interactions